INCONCRETO NEWS
Generative AI in Business: The European Race for Responsible Adoption
Why does this matter?
Generative AI, as a term, refers to artificial intelligence that has been specifically built to generate new content in one form or another. Unlike traditional AI systems focused on classification or prediction, generative AI creates novel content, including text, image, video, audio, and code, instead of merely recognizing or predicting outcomes.
Generative AI — powered by models such as ChatGPT, Mistral, Claude or Gemini — is increasingly embedded in the daily operations of businesses. Whether through content generation, code development, HR support, customer service automation or decision-making tools, use cases are multiplying at speed.
As this technology reshapes work across industries, Europe is charting its own path: one that seeks to balance innovation with ethical regulation and digital sovereignty. In this shifting landscape, organisations must rethink their strategies and operating models. The challenge is clear: to harness the promise of AI while ensuring responsible adoption.
Unlike other regions, Europe is advancing with a firmly regulated framework. The AI Act, adopted in 2024, ensures that Europeans can trust what AI has to offer. It sets mandatory standards around ethics, transparency and accountability. For European businesses, this creates a dual imperative: to embrace cutting-edge technologies while remaining fully compliant with evolving regulations.
This is not just a matter of compliance — it’s a strategic question. Businesses must consider how to deploy AI tools in ways that are secure, transparent, and aligned with their values.
The ability to do so is becoming a key differentiator. This evolving landscape presents a valuable opportunity for advisory firms. From regulatory alignment and workforce training to integration strategies and innovation roadmaps, the demand for expert guidance is growing.
At INCONCRETO, we help organisations navigate this complexity — not just to adopt generative AI, but to do so responsibly, confidently and with purpose.
Generative AI: A Technological Breakthrough Already in Motion
Since 2023, generative AI has progressed far beyond the experimental stage. It is now embedded in the day-to-day operations of organisations. It writes, codes, summarises, imagines. Internally, it rewrites procedures, automates meeting notes, and generates training materials. Externally, it fuels content strategies, enhances customer relations, and supports industry-specific diagnostics.
Across both large corporates and SMEs, generative AI has evolved from a novelty to a transformative tool.
Its use cases are expanding rapidly:
- In Human Resources, it drafts job descriptions, assists with interview preparation, streamlines CV screening, and personalises training programmes.
- In IT, tools such as GitHub Copilot or Cody act as programming assistants, boosting developer productivity.
- In Marketing and Communications, it enables large-scale, multilingual content production — from articles and social posts to visuals and video.
- In Customer Support, it powers more fluent, multilingual chatbots capable of providing 24/7, contextualised, and consistent responses.
Some of the most compelling real-world applications of generative AI include:
- Healthcare and Life Sciences:Insilico Medicine used generative AI to identify a novel drug candidate for fibrosis. Their platform designed the molecule in under 46 days, compared to the typical 12–18 months. The model analysed protein targets and proposed viable compounds, dramatically accelerating drug discovery.
- E-commerce: Generative AI is being used to create dynamic product descriptions, automate ad creatives, and generate personalised recommendations at scale. Marks & Spencer, a leading UK retailer, has integrated generative AI to personalise the online shopping experience. The system offers tailored fashion advice based on individual body types and style preferences. Over 450,000 users have completed a style quiz that generates outfit suggestions from 40 million combinations. Additionally, M&S has automated 80% of its product descriptions, contributing to a 7.8% increase in online fashion and homeware sales over the past year.
- Marketing and Advertising: Coca-Cola leveraged OpenAI and Bain’s generative AI tools to produce video and image content for its “Create Real Magic” campaign. The initiative led to a 40% increase in user-generated content submissions and social engagement, illustrating how generative design can enhance brand interaction.
In an interview with Marketing Dive, published March 10, 2025, Pratik Thakar, Global Vice President and Head of Generative AI at Coca-Cola, recalled:
“We started our generative AI creative incubator, in late ’22, and that’s when GPT got launched and the whole hype cycle started. Bain is our consulting partner, and they came up with this proposal of collaborating with OpenAI, and we were the first to raise our hand and say, “Yes, we want to be part of it.”
A Distinctively European Approach: Regulated and Responsible Innovation
Unlike other regions, Europe is forging its own path in AI adoption by placing regulation and ethics at the heart of its strategy. The cornerstone of this approach is the AI Act, adopted in 2024, with gradual implementation through 2026. It is the world’s first comprehensive legal framework for artificial intelligence.
The EU AI Act stands as a pioneering regulation designed to govern artificial intelligence systems, placing a strong emphasis on upholding fundamental rights, and preventing potential AI-induced harm.
Notably, the Act classifies AI systems into four risk levels, from minimal to unacceptable, and sets out strict obligations for high-risk systems, particularly general-purpose AI models, such as generative AI. It requires safety, governance, and human oversight throughout the AI lifecycle. It also mandates transparency obligations on AI models, including clear labelling of AI-generated content.
While its immediate impact is felt within the European market, the influence of the EU AI Act extends globally, representing a significant milestone in AI regulation.
This regulatory foundation is reinforced by other key instruments:
- The GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation ), which remains essential whenever personal data is involved.
- The NIS 2 Directive, securing network and information systems
- New EU rules also prioritise traceability, model explainability, and environmental sustainability — including the carbon footprint of training large models.
For businesses, this means innovation must go hand in hand with compliance, as they build AI that is trustworthy, transparent, and aligned with European values.
The EU’s position stands in sharp contrast to the more permissive stance of the United States or the state-driven model in China. Europe is betting on a form of leadership rooted in responsibility, not just speed.
“The AI Act (Regulation (EU) 2024/1689 laying down harmonised rules on artificial intelligence) is the first-ever comprehensive legal framework on AI worldwide. The aim of the rules is to foster trustworthy AI in Europe”
— European Commission, 2024
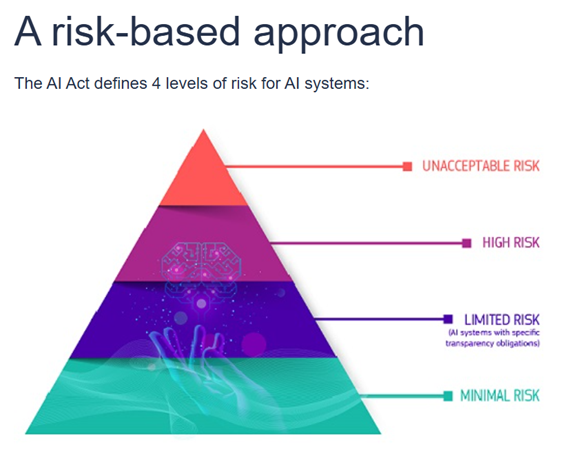
Integrating AI Responsibly: Towards a New Enterprise Strategy
Adopting generative AI today is no longer simply a matter of innovation — it is a strategic imperative. Any organisation looking to integrate these tools must now meet several parallel challenges:
- Identify use cases that align with its core business activities;
- Ensure regulatory compliance — including traceability, consent, data protection, and system auditability;
- Manage the social impact — through training, upskilling, and stakeholder engagement;
- Maintain alignment with the company’s values and overarching purpose.
Meeting these demands requires deep, structural work: a rethink of data governance, the creation of risk assessment protocols, and often, a broader organisational reconfiguration. All of this must happen within a shifting landscape, where technology is evolving faster than legislation — and faster than cultural norms can adapt.
In this context, successful integration of generative AI will depend on the organisation’s ability to bridge the gap between technology, ethics, legal frameworks, and human considerations.
Consulting Firms: Catalysts for Responsible Adoption
In this transition, consulting firms have a pivotal role to play.
Far from techno-centric approaches, their mission is to support organisations through a lens of strategic alignment:
- Mapping potential use cases and assessing their relevance to the business,
- Ensuring compliance with European regulatory frameworks,
- Training teams to develop a culture of technological discernment,
- Designing responsible innovation approaches that take into account environmental impact, systemic bias, and sovereignty concerns.
In an environment where technology evolves in successive waves, value no longer lies in the tools themselves, but in the ability to integrate them intelligently, sustainably, and with a human perspective.
INCONCRETO’s Strategic Vision
Generative AI is not a passing trend. It marks a fundamental shift in value chains, professions, and the way organisations imagine their future.
At INCONCRETO, we believe that responsible adoption of these technologies begins with an informed dialogue between strategy, ethics, and operations. It is this intersection — between innovation and clarity — that will enable European companies not only to transform themselves, but to build lasting resilience in an increasingly algorithm-driven world.
Pour en savoir plus, vous pouvez consulter les sources ci-dessous
- https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/policies/regulatory-framework-ai#:~:text=Latest%20News,DIGIBYTE%20%7C%2030%20June%202025
- https://www.marketingdive.com/news/what-coca-cola-learned-generative-ai/741709/
- https://singularityhub.com/2023/06/28/a-drug-designed-entirely-by-ai-is-starting-its-first-human-trials/
- https://www.economie.gouv.fr/entreprises/assurer-sa-cybersecurite-et-la-protection-de-ses-donnees/le-reglement-general-sur-la#
- https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/policies/nis2-directive
Latest News
Semiconductors Today: Global Industry Dynamics and Strategic Value Chains

Mining Today, Powering Tomorrow: The Global Race for Transition Minerals
Newsletter
© INCONCRETO. All rights reserved. Powered by AYM